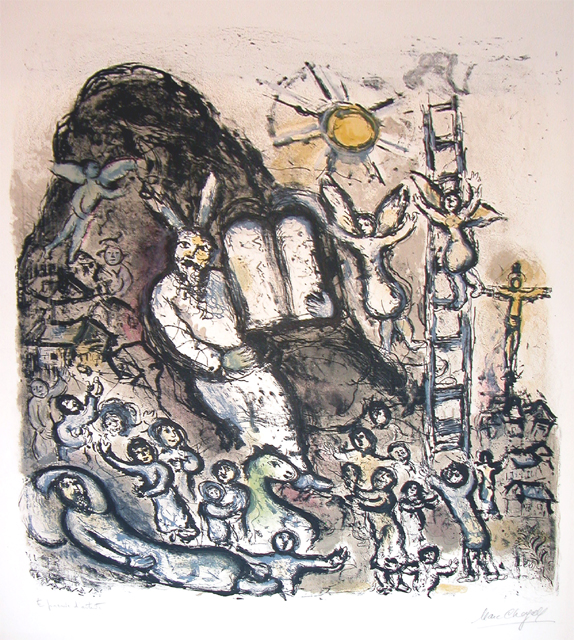
Marc Chagall (6 July 1887 – 28 March 1985), was a Russian-French artist associated with several major artistic styles and one of the most successful artists of the 20th century. He was an early modernist and created works in virtually every artistic medium, including painting, book illustrations, stained glass, stage sets, ceramic, tapestries and fine art prints.
Art critic Robert Hughes referred to Chagall as "the quintessential Jewish artist of the twentieth century." According to art historian Michael J. Lewis, Chagall was considered to be "the last survivor of the first generation of European modernists." For decades, he "had also been respected as the world's preeminent Jewish artist." Using the medium of stained glass, he produced windows for the cathedrals of Reims and Metz, windows for the UN, and the Jerusalem Windows in Israel. He also did large-scale paintings, including part of the ceiling of the Paris Opéra.
Before World War I, he traveled between St. Petersburg, Paris, and Berlin. During this period he created his own mixture and style of modern art based on his idea of Eastern European Jewish folk culture. He spent the wartime years in Soviet Belarus, becoming one of the country's most distinguished artists and a member of the modernist avante-garde, initiating the Vitebsk Arts College before leaving again for Paris in 1922.
He had two basic reputations, writes Lewis: as a pioneer of modernism and as a major Jewish artist. He experienced modernism's "golden age" in Paris, where "he synthesized the art forms of Cubism, Symbolism, and Fauvism, and the influence of Fauvism gave rise to Surrealism." Yet throughout these phases of his style "he remained most emphatically a Jewish artist, whose work was one long dreamy reverie of life in his native village of Vitebsk." "When Matisse dies," Pablo Picasso remarked during the 1950s, "Chagall will be the only painter left who understands what color really is."